Watch out for fake PayPal invoices in your email! Though this particular scam is not new, it appears to be making a strong comeback as of late. Read on to learn more about this scheme so you can keep your money safe. In general, add an extra dose of skepticism when you receive requests for money or sensitive personal information.
What should I be on the lookout for?
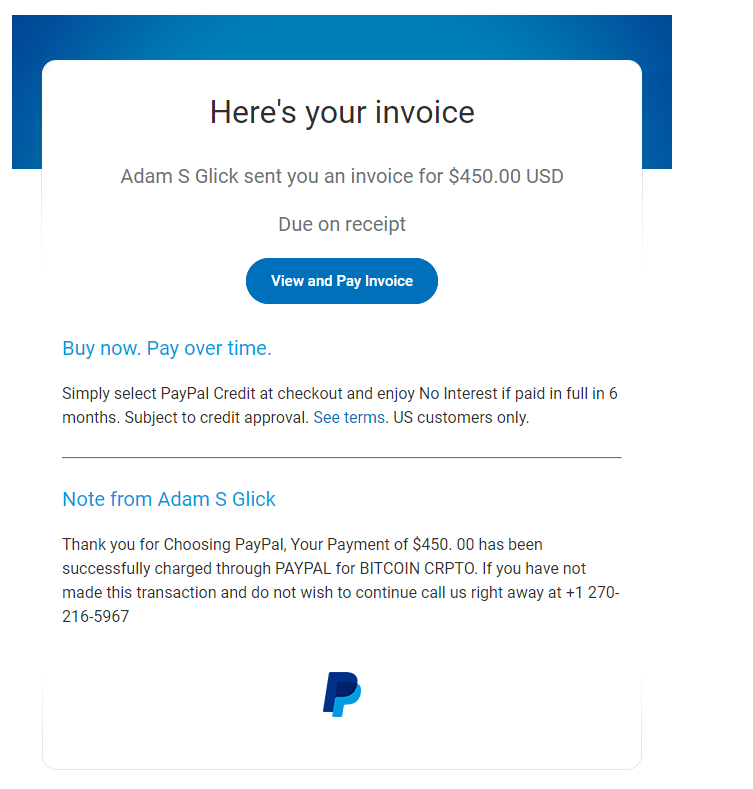
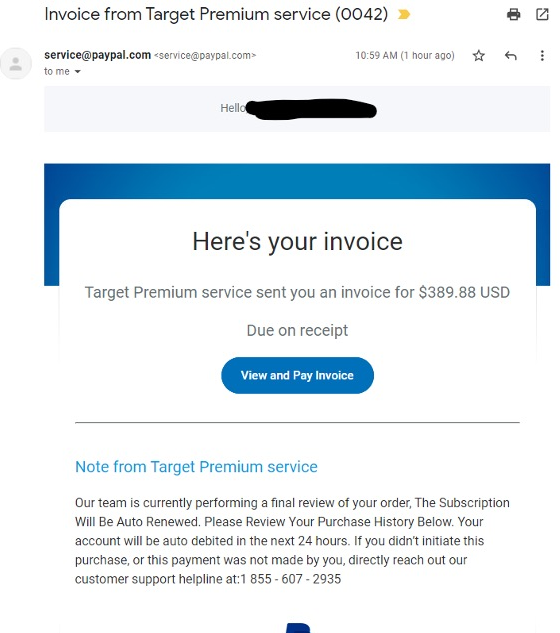
Watch out for invoices sent using PayPal (services[@]paypal[.]com) for products or services you did not acquire and cannot associate with a specific purchase. The payment requests may leverage well known companies (e.g. Amazon Prime subscription), claim that you have successfully purchased cryptocurrency, or simply come from an unknown individual. The message will likely include a phone number to call for a “refund” (don’t do this!).
If I receive this, how should I handle it?
Most importantly, do not pay the invoice! Since the invoice will actually show up on the PayPal account linked to your email address, if you click the link to pay (and have payment methods set up within PayPal), the money will immediately be transferred to the scammers. If you were a victim of this scam, open a dispute and/or escalate it to a claim on PayPal’s site.
Secondly, do not call the number! Remember, an invoice is essentially a bill or a request for payment, NOT a confirmation of payment. The note in the message will make it seem as though the payment has been processed or is already pending unless you call their phone number. Instead of refunding the transaction (which never occurred), the scammer on the phone will likely direct you to install software that allows them to control your device at which point they may try to gain access to your financial accounts or steal your credentials.
Lastly, don’t forget to report the phishing email. To help Technology Services help other campus members, forward the phishing email as an attachment to servicedesk@pugetsound.edu. It may also be beneficial to report it to PayPal.
What makes this scam difficult to spot?
If you’ve talked to anyone in Technology Services, you’ve probably received advice to look closely at the sender’s email address to identify fraudulent messages. However, that does not help in this instance. The message comes from services[@]paypal[.]com and is technically a real invoice created with PayPal. Unfortunately, all it takes is a scammer to use PayPal’s free invoice template service and set your email as the customer email address to carry out this scam.
Examples